Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Tomoya*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Kobayashi, Toru; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Narita, Hirokazu*
Analytical Sciences, 35(12), p.1353 - 1360, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.17(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Futakawa, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 13th International Symposium on Advanced Science and Technology in Experimental Mechanics (13th ISEM'18) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
Issues on the engineering technologies relating to high-power spallation neutron sources with liquid metals are introduced. The present status on research activities and results was reviewed.
Itami, Toshio*; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
Metals, 5(3), p.1212 - 1240, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:4.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A new kind of suspension liquid was developed by dispersing Ti nanoparticles (10 nm) in liquid Na, which was then determined by TEM (transmission electron microscopy) analysis. The volume fraction was estimated to be 0.0088 from the analyzed Ti concentration (2 at.%) and the densities of Ti and Na. This suspension liquid, Liquid Sodium containing nanoparticles of titanium (LSnanop), shows, despite only a small addition of Ti nanoparticles, many striking features, namely a negative deviation of 3.9% from the ideal solution for the atomic volume, an increase of 17% in surface tension, a decrease of 11% for the reaction heat to water, and the suppression of chemical reactivity to water and oxygen. The decrease in reaction heat to water seems to be derived from the existence of excess cohesive energy of LSnanop. The excess cohesive energy was discussed based on simple theoretical analyses, with particular emphasis on the screening effect. The suppression of reactivity is discussed with the relation to the decrease of heat of reaction to water or the excess cohesive energy, surface tension, the action as a plug of Ti oxide, negative adsorption on the surface of LSnanop, and percolation.
Shimada, Michiya; Hirooka, Yoshihiko*
Nuclear Fusion, 54(12), p.122002_1 - 122002_7, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:86.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Tungsten is considered to be the most promising material for divertor in a fusion reactor. Tungsten divertor can withstand the heat loads of ITER, but the heat loads of DEMO divertor is a challenge. Pulsive heat loads as those associated with disruption could melt tungsten targets. The surface would not be flat after subsequent resolidification, which would significantly deteriorate its heat handling capability. Furthermore, DBTT of tungsten is rather high:  400
400 C, which would become even higher after neutron irradiation, possibly resulting in cracks in tungsten. Our proposal is to use liquid metal for the divertor target material and actively circulate it with
C, which would become even higher after neutron irradiation, possibly resulting in cracks in tungsten. Our proposal is to use liquid metal for the divertor target material and actively circulate it with 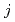

 force. A simplified analysis of mhd equation in a cylindrical geometry suggests that the engineering requirement is modest. This analysis suggests that this new divertor concept merits further investigation.
force. A simplified analysis of mhd equation in a cylindrical geometry suggests that the engineering requirement is modest. This analysis suggests that this new divertor concept merits further investigation.
Morimoto, Yoshiki*; Kato, Sayuri*; Toda, Naohiro*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Yaoita, Kenichi*; Shimomura, Osamu
Review of High Pressure Science and Technology, 7, p.245 - 247, 1998/03
X-ray diffraction for liquid Rb and liquid Na has been measured under pressure up to 6 GPa using synchrotron radiation. Volume dependences of static structure factor 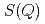 and pair distribution function
and pair distribution function 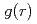 were obtained to the volume range
were obtained to the volume range 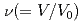 of 0.52 for liquid Rb and
of 0.52 for liquid Rb and  of 0.73 for liquid Na to investigate the effect of the electronic change on the structure of liquid metals. With increasing pressure, the peaks of
of 0.73 for liquid Na to investigate the effect of the electronic change on the structure of liquid metals. With increasing pressure, the peaks of 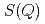 of both liquid Rb and liquid Na shift towards higher
of both liquid Rb and liquid Na shift towards higher  , and the heights of the first peak increase. Theses volume dependences of the structural data are compared with those for other metals under pressure and expanded fluids.
, and the heights of the first peak increase. Theses volume dependences of the structural data are compared with those for other metals under pressure and expanded fluids.
; Chihara, Junzo
Molecular Simulation, 16, p.31 - 46, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.3(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo
Oyo Butsuri, 44(8), P. 877, 1975/08
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo;
Bussei Kenkyu, 19(5), p.B35 - B45, 1973/05
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo
Kosoku Denjiekiryu Ni Kansuru Chosa Hokokusho, p.159 - 170, 1973/00
no abstracts in English
Proc.2nd Int.Conf. on the Properties of Liquid Metals, p.137 - 141, 1972/00
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo
Proc.2nd Int.Conf.Properties Liquid Metals, p.461 - 465, 1972/00
no abstracts in English
Ueda, Yuki
no journal, ,
The separation and recovery of PGM is carried out by a hydrometallurgy process mainly based on a solvent extraction method. In recent years, development of alternative solvents for such volatile organic solvents has been advanced. Ionic liquids (IL) has attracted substantial interest in many fields as a green alternative solvent due to their non-volatile, non-flammable, and thermally stable properties. Task-specific ionic liquids (TSIL) that functionalized by incorporating ligating group can give the extraction ability for metal ions. Many extraction systems using IL and TSIL aimed at separating PGM have been reported so far, however there is no extraction system that achieves individual separation of Pd and Pt by one type of TSIL. In this study, imidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide type TSIL incorporating a urea group was synthesized and its extraction ability for Pd and Pt was evaluated from a viewpoint the individual separation of Pd and Pt.